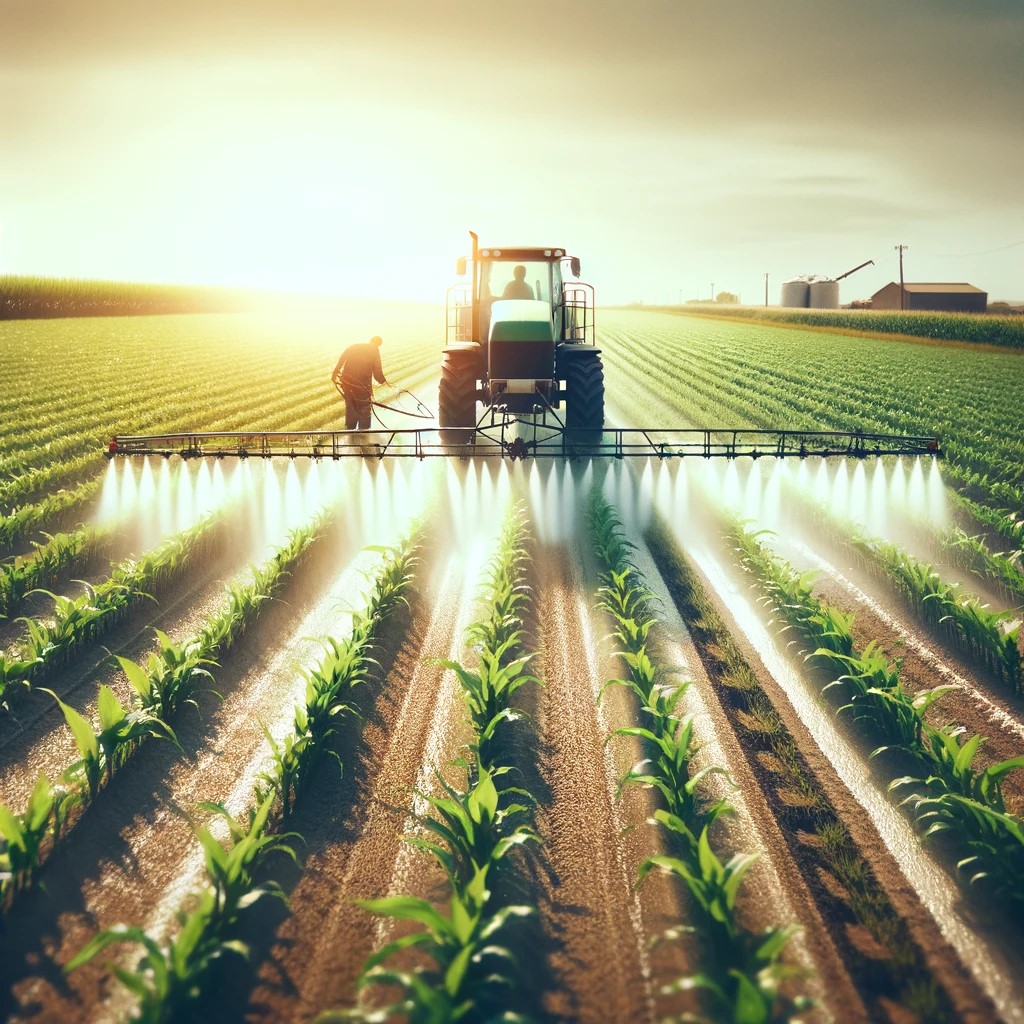
Paraquat, also known by its trade name Gramoxone, is a widely used herbicide employed extensively in agriculture, particularly by commercial farmers for weed and grass management. Its popularity stems from its efficacy, especially against plants that have developed resistance to glyphosate, the primary ingredient in Roundup. This concentrated herbicide is meticulously mixed with water and applied as a spray to agricultural crops.
Globally, approximately 377 companies are involved in the production of paraquat products, with Syngenta’s Gramoxone being a notable brand in the United States. However, despite its effectiveness, Paraquat poses significant health risks, both in the short term and long term, with potential fatal consequences. Moreover, research suggests a potential link between prolonged exposure to Paraquat and the development of Parkinson’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder affecting motor function.
Since its introduction in 1964, Paraquat has been a staple tool for commercial farmers and agricultural workers in managing invasive weeds and grasses, primarily in crops like corn, soy, and cotton. Due to its extreme toxicity, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has imposed stringent regulations, limiting its application to licensed practitioners in commercial settings, with no authorization granted for homeowner use. The EPA underscores the severe dangers associated with Paraquat, labeling it as “one sip can kill.”
Careful handling and adherence to safety protocols are paramount when using Paraquat, particularly ensuring it is not utilized around crops susceptible to contamination. Licensed applicators face the highest risk of exposure, although anyone working in areas where Paraquat is applied, including farmers, groundskeepers, and agricultural laborers, may be at risk. Paraquat products in the U.S. incorporate multiple safety features, including dyes, odors, and chemicals to deter accidental ingestion, along with agents to induce vomiting to mitigate harm.
Symptoms of Paraquat exposure vary depending on the level and method of contact, with acute poisoning symptoms manifesting rapidly upon substantial ingestion, potentially leading to fatality. These symptoms encompass a range of complications, including respiratory issues, gastrointestinal distress, heart and kidney failure, seizures, and localized swelling. Prolonged exposure to Paraquat can result in chronic health effects affecting various organs, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, and potentially increasing the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Paraquat poisoning can occur through ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact, with accidental ingestion being the most common scenario, often resulting in fatal outcomes. Unfortunately, there is no known antidote to counteract its toxic effects. Studies have suggested a correlation between Paraquat exposure and the development of Parkinson’s disease, attributed to oxidative stress-induced damage to dopamine-producing neurons.
It’s essential to distinguish Paraquat from Roundup, with Paraquat being significantly more toxic than glyphosate, the active ingredient in Roundup. Despite being phased out or banned in several countries, Paraquat’s usage in the U.S. has increased notably due to its efficacy against glyphosate-resistant weeds. The EPA periodically reassesses pesticides, and while Paraquat has been reaffirmed for restricted use, stricter safety measures have been proposed to mitigate health and environmental risks.
In the event of Paraquat poisoning, urgent medical attention is crucial, as there is no specific antidote available. Treatment involves removing Paraquat from the body and providing supportive care measures to manage symptoms and complications. Prompt washing of skin exposed to Paraquat and immediate medical attention for eye exposure are recommended.
In conclusion, while Paraquat remains a potent herbicide for agricultural use, its significant toxicity and potential health risks, including its association with Parkinson’s disease, underscore the importance of stringent regulations, safety measures, and heightened awareness among users.