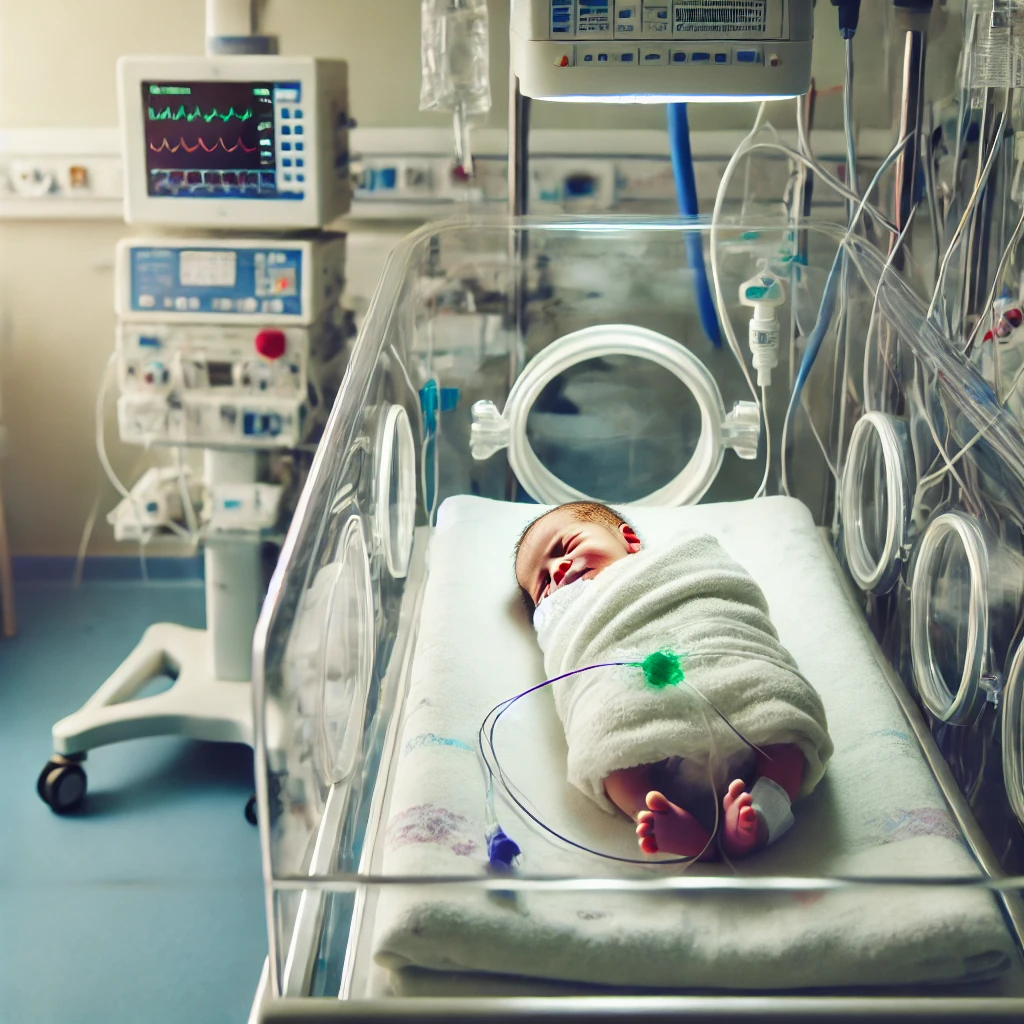
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a severe gastrointestinal condition primarily affecting premature infants. Characterized by inflammation and bacterial invasion of the intestine, NEC can lead to devastating consequences, including perforation of the bowel and systemic infection. Parents of affected infants often face overwhelming stress and uncertainty as they navigate their child’s medical crisis. Understanding NEC, its causes, and potential legal implications is crucial for those seeking justice and support.
At Mass Tort America, we recognize the immense burden that NEC places on families. Our experienced team is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of medical and legal challenges. We provide comprehensive legal support to families across the nation, ensuring you have the resources and guidance necessary to pursue rightful compensation.
What Is Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)?
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a serious condition that typically develops in premature infants within the first few weeks of life. It primarily affects premature babies and low birthweight infants, and the exact cause remains unclear. However, several risk factors have been identified, including prematurity, formula feeding, and a compromised immune system. NEC starts with inflammation of the intestinal wall, which can progress to tissue death and perforation, leading to severe infection and other complications in the abdominal cavity. The condition significantly affects babies born prematurely, who are more vulnerable to developing NEC due to their underdeveloped gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of NEC can vary but often include abdominal distension, feeding intolerance, bloody stools, and lethargy. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to improving outcomes. Diagnostic methods typically include imaging studies and blood tests. Treatment may involve stopping oral feedings, providing total parenteral nutrition to allow the intestines to heal, and administering antibiotics to combat infections. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged portion of the intestine. Monitoring for complications such as bowel perforation, which can lead to infection of the abdominal cavity, is crucial. Breastfeeding infants is highly encouraged, as human milk contains healthy bacteria and other components that help fight bacterial infections and support the gastrointestinal tract, thereby reducing the risk of NEC.
The prognosis for infants with NEC depends on the severity of the condition and the promptness of treatment. While some infants recover fully with appropriate medical care, others may suffer long-term health issues or complications. Understanding these aspects of NEC is essential for parents and caregivers to make informed decisions about their child’s care. The protective effects of breast milk are particularly important, as it contains nutrients and antibodies that help premature babies develop a stronger immune system and a healthier gastrointestinal tract. In contrast, formula feeding has been associated with a higher risk of NEC, underscoring the importance of promoting breastfeeding, especially for low birthweight and premature infants.
Potential Causes And Risk Factors
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a serious disease that primarily affects premature newborns. While the exact cause of NEC remains unknown, research suggests that a combination of factors contributes to its development. Prematurity is one of the most significant risk factors, as premature infants have underdeveloped bowel function and intestinal barrier function. These underdeveloped systems make them more susceptible to intestinal inflammation and bacterial infection. NEC typically occurs in premature babies within the first few weeks of life while they are still in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Other risk factors include patent ductus arteriosus, which can affect blood flow to the intestines, and respiratory failure, which can decrease the oxygen supply to the bowel wall.
Enteral feedings, particularly when infants are fed formula rather than breast milk, have also been associated with a higher risk of developing necrotizing enterocolitis. Breast milk contains nutrients and antibodies that support intestinal barrier function and help prevent inflammation, whereas formula can be harder for a premature baby to digest and may disrupt the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut. Symptoms of Necrotizing Enterocolitis can include abdominal distention, abdominal tenderness, and systemic signs such as lethargy and temperature instability. These symptoms can be challenging to distinguish from other common issues in premature newborns, making early diagnosis and intervention critical. Diagnostic tools such as imaging studies, blood tests to check for changes in red blood cells, and a breath hydrogen test can help identify NEC and assess the severity of the condition. An abnormal gas pattern, seen as air bubbles in the baby’s intestines, is a hallmark sign of NEC.
Complications of NEC can be severe and include bowel perforation, which allows bacteria to escape into the abdominal cavity, leading to infection and inflammation. Air bubbles in the wall of the intestine, known as pneumatosis intestinalis, are a hallmark sign of NEC and can be detected through imaging studies. In some cases, NEC can lead to intestinal stricture or short bowel syndrome, both of which can affect a baby’s long-term bowel function and nutrient absorption. Treatment often involves stopping enteral feedings, placing a nasogastric tube to decompress the stomach, and providing intravenous nutrition. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the small and large intestines. Some infants may require a bowel transplant if extensive damage occurs. Monitoring a child’s belly for signs of distention and changes in the baby’s poop can help in early detection and treatment.
While the exact cause of NEC remains unknown, research suggests that a combination of factors contributes to its development. Premature birth is the most significant risk factor, as premature infants have underdeveloped intestines and immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections and inflammation. Formula feeding has also been linked to an increased risk of NEC compared to breastfeeding, which provides protective antibodies and promotes healthy gut bacteria. Genetic factors may play a role in predisposing certain infants to NEC. Studies have shown that siblings of infants with NEC are at a higher risk, indicating a possible genetic component. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as congenital heart disease or low blood flow to the intestines, can increase the likelihood of developing NEC. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for preventing NEC. Parents and healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring premature infants for early signs of the condition. Prompt medical intervention, including the administration of extra oxygen to ensure adequate oxygenation of the bowel wall, can significantly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Legal Implications And Pursuing Justice
The development of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in premature infants raises significant legal questions, particularly regarding the role of formula feeding. Numerous lawsuits have been filed against formula manufacturers, alleging that their products contribute to the risk of NEC. These cases often argue that the manufacturers failed to adequately warn parents and healthcare providers about the potential dangers of using their products in premature infants. When a premature infant is diagnosed with NEC, it is crucial to investigate whether the use of formula was a factor and if proper warnings were provided. The legal implications can be profound, as proving negligence or failure to warn can result in substantial liability for the manufacturers.
Families affected by NEC may be entitled to compensation for medical expenses, pain and suffering, and long-term care costs. Legal claims can also seek damages for emotional distress and loss of future earnings if the infant suffers permanent disabilities. Pursuing legal action can help hold negligent parties accountable and provide financial relief to families facing significant medical and caregiving challenges. In addition to product liability claims against formula manufacturers, medical malpractice claims can be filed against healthcare providers if there is evidence that the standard of care in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) was not met. This includes ensuring timely diagnosis and appropriate management of NEC symptoms and adhering to best practices for feeding premature infants.
It’s important to consult with an experienced attorney who specializes in medical malpractice and product liability cases to explore your legal options. An attorney can help gather evidence, navigate complex legal processes, and advocate for your family’s rights. Understanding the legal landscape is essential for seeking justice and ensuring that responsible parties are held accountable for their actions. By pursuing legal action, parents not only seek justice for their child but also contribute to improving medical practices and product safety standards, potentially preventing future cases of NEC in other infants born prematurely.
How Mass Tort America Can Help
At Mass Tort America, we understand the profound impact that NEC can have on families. Our dedicated legal team is committed to providing compassionate and comprehensive support to those affected by this devastating condition. We have extensive experience handling complex medical and product liability cases, ensuring that your family receives the best possible representation.
Our concierge team is available to assist you with all aspects of your case, from gathering medical records to coordinating with expert witnesses. We work tirelessly to build a strong case on your behalf, aiming to secure the compensation you deserve. With Mass Tort America, you can focus on your child’s health and well-being while we handle the legal complexities.
If your family has been affected by NEC, don’t hesitate to reach out for help. Contact Mass Tort America today at 800-356-4338 or visit our contact form at https://masstortamerica.com/contact/. We are here to support you every step of the way.